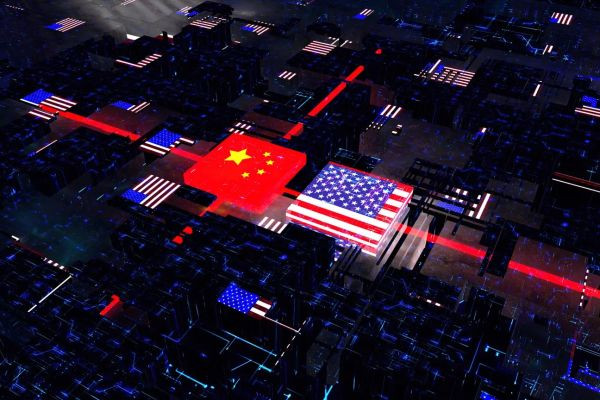
In a move that could have far-reaching consequences for the global tech industry and US-China relations, China has recently implemented restrictions on the export of key semiconductor materials. This decision comes as the chip war between China and the United States intensifies, with both nations vying for dominance in the semiconductor sector, which is crucial for modern technology.
The Restriction Measure:
Under the new restriction measure, China will tightly control the export of certain critical semiconductor materials. These materials are vital components in the manufacturing of advanced chips used in various electronic devices, including smartphones, computers, artificial intelligence systems, and military equipment. By placing limits on the export of these materials, China aims to safeguard its own technological advancements and reduce its reliance on foreign suppliers.
The Escalating Chip War:
The chip war between China and the US has been simmering for years, but recent geopolitical tensions have exacerbated the situation. Both countries view the semiconductor industry as a crucial element of national security and economic competitiveness. With technological supremacy and innovation at stake, the competition has intensified, leading to a series of restrictive measures and countermeasures by both sides.
Impact on Global Trade and Tech Industry:
The restrictions imposed by China on semiconductor materials are likely to trigger supply chain disruptions across the global tech industry. Many companies in the United States and other countries rely on these materials for their chip production. As China is a major player in the semiconductor market, these restrictions could lead to shortages, increased costs, and delays in production for various technology manufacturers worldwide.
Furthermore, the semiconductor industry is deeply interconnected, with supply chains spanning multiple countries. Any disruptions in one part of the supply chain can have a cascading effect, impacting companies in other nations. This interdependence poses a significant challenge for businesses and policymakers seeking to mitigate the consequences of China's actions.
National Security and Geopolitics:
The chip war is not solely about economic interests; it also has significant implications for national security and geopolitical dynamics. Semiconductors play a crucial role in modern warfare, defense systems, and critical infrastructure. As such, both China and the US perceive control over the supply of these key materials as essential for their strategic interests.
The restrictions imposed by China could lead to heightened tensions with the US and its allies, who may perceive the move as an attempt to gain a competitive edge in the technology arms race. It may also prompt the US to respond with its own measures, potentially escalating the conflict further and creating a broader rift in already fragile US-China relations.
Navigating the Future:
As the chip war continues to unfold, governments and technology companies worldwide will face complex challenges in navigating the shifting landscape of global trade and technological competition. Diversifying supply chains, investing in domestic semiconductor production, and fostering international collaboration on technology standards and regulations may become crucial strategies for mitigating the impact of China's semiconductor material restrictions.
Ultimately, finding a balance between economic interests, national security concerns, and geopolitical stability will be paramount in resolving the chip war and shaping the future of the tech industry on a global scale. The decisions made in response to these restrictions could have lasting implications for the world's technological development and international relations.
The Race for Technological Supremacy:
The semiconductor industry is a pivotal battleground in the race for technological supremacy between China and the US. Both countries have made significant investments in research and development, with China striving to reduce its dependence on foreign technology and achieve self-sufficiency in semiconductor manufacturing. Meanwhile, the US seeks to maintain its leadership position in the tech sector and protect its technological innovations from foreign competition.
The competition for dominance in the semiconductor industry has led to increased scrutiny and regulation of technology transfers and intellectual property rights. The US has taken measures to restrict the export of advanced chip-making equipment and software to China, citing concerns over the potential misuse of technology for military applications. In response, China has sought to develop its indigenous semiconductor manufacturing capabilities and promote homegrown technology champions.
Potential Risks and Opportunities:
The escalating chip war and restrictions on semiconductor materials pose risks and opportunities for various stakeholders in the tech industry. For companies heavily reliant on the Chinese market or Chinese suppliers for semiconductor components, the new restrictions may lead to market uncertainties and disruptions in their supply chains. These companies might need to reassess their sourcing strategies and consider diversifying their supply chains to mitigate risks.
On the other hand, the restrictions on semiconductor materials could present opportunities for other countries to step in and fill the void left by China's reduced exports. Semiconductor manufacturers in countries such as South Korea, Taiwan, and the European Union may witness increased demand as companies seek alternative suppliers. This could potentially enhance their competitiveness and strengthen their position in the global semiconductor market.
Cooperation and Trade Negotiations:
Amidst the mounting tensions, there might still be opportunities for dialogue and cooperation between China and the US to find common ground on semiconductor technology and trade-related issues. Engaging in constructive negotiations and addressing concerns around intellectual property rights and market access could lead to a more stable and predictable environment for the tech industry.
International organizations, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), may also play a role in facilitating discussions and mediating disputes related to semiconductor trade and technology restrictions. Collaborative efforts to establish clear rules and norms for the global semiconductor market could help prevent further escalations in the chip war and promote fair competition among nations.
Long-term Implications for Innovation:
The outcome of the chip war and the decisions made regarding semiconductor materials' restrictions could have profound long-term implications for innovation and technological progress. While restrictions may provide temporary advantages for one nation, they could also stifle the cross-border flow of ideas and knowledge, hindering overall technological advancement.
In contrast, an open and collaborative approach to technological development, where ideas, talent, and expertise can freely circulate, can foster innovation and lead to breakthroughs that benefit the entire world. Striking a balance between safeguarding national interests and fostering global innovation remains a critical challenge for policymakers and industry leaders alike.
Conclusion:
The recent restrictions imposed by China on key semiconductor materials amid the escalating chip war with the US underscore the critical role of technology in contemporary geopolitics and global trade. The implications of these actions are vast, affecting industries, economies, and international relations. Navigating the complexities of the chip war will require careful diplomacy, innovative strategies, and a deep understanding of the interconnectedness of the global tech industry. Only through collaborative efforts and a commitment to constructive dialogue can nations hope to find common ground and shape a future where technological innovation can thrive while addressing legitimate concerns around national security and economic competitiveness.
 Bitcoin: $97675.00 1.54%
Bitcoin: $97675.00 1.54%  Ethereum: $3414.51 2.98%
Ethereum: $3414.51 2.98%  Tether: $1.00 0.08%
Tether: $1.00 0.08%  Solana: $256.23 0.19%
Solana: $256.23 0.19%  BNB: $654.92 5%
BNB: $654.92 5%  XRP: $1.46 0.26%
XRP: $1.46 0.26%  Dogecoin: $0.43 4.2%
Dogecoin: $0.43 4.2%  USDC: $1.00 0.12%
USDC: $1.00 0.12%  Cardano: $1.05 7.78%
Cardano: $1.05 7.78%  Lido Staked ETH: $3397.51 2.63%
Lido Staked ETH: $3397.51 2.63%  TRON: $0.21 6.63%
TRON: $0.21 6.63%  Avalanche: $42.37 7.81%
Avalanche: $42.37 7.81%  Stellar: $0.51 68.61%
Stellar: $0.51 68.61%  Shiba Inu: $0.00 2.54%
Shiba Inu: $0.00 2.54%  Wrapped Bitcoin: $97534.77 1.4%
Wrapped Bitcoin: $97534.77 1.4%  Polkadot: $8.54 35.67%
Polkadot: $8.54 35.67%  Chainlink: $17.48 12.1%
Chainlink: $17.48 12.1%  Bitcoin Cash: $508.55 4.12%
Bitcoin Cash: $508.55 4.12%  UNUS SED LEO: $8.61 1.99%
UNUS SED LEO: $8.61 1.99%  NEAR Protocol: $6.17 8.61%
NEAR Protocol: $6.17 8.61%  Litecoin: $98.61 9.03%
Litecoin: $98.61 9.03%  Uniswap: $10.87 15.06%
Uniswap: $10.87 15.06%  Internet Computer: $11.41 10.44%
Internet Computer: $11.41 10.44%  Multi Collateral DAI: $1.00 0.01%
Multi Collateral DAI: $1.00 0.01%  Crypto.com Coin: $0.20 4.08%
Crypto.com Coin: $0.20 4.08%  Sp8de: $0.59 12.75%
Sp8de: $0.59 12.75%  Ethereum Classic: $29.69 6.55%
Ethereum Classic: $29.69 6.55%  Artificial Superintelligence Alliance: $1.39 12.74%
Artificial Superintelligence Alliance: $1.39 12.74%  VeChain: $0.04 27.54%
VeChain: $0.04 27.54%  Filecoin: $5.41 14.48%
Filecoin: $5.41 14.48%  Stacks: $2.10 7.02%
Stacks: $2.10 7.02%  OKB: $50.71 10.64%
OKB: $50.71 10.64%  Monero: $160.46 1.21%
Monero: $160.46 1.21%  Aave: $176.48 6.86%
Aave: $176.48 6.86%  Fantom: $0.89 23.71%
Fantom: $0.89 23.71%  Algorand: $0.30 21.04%
Algorand: $0.30 21.04%  The Graph: $0.24 11.46%
The Graph: $0.24 11.46%  Hedera Hashgraph: $0.15 11.8%
Hedera Hashgraph: $0.15 11.8%  Injective: $27.99 13.91%
Injective: $27.99 13.91%  Cosmos: $8.17 11.36%
Cosmos: $8.17 11.36%  THORChain: $5.63 6.72%
THORChain: $5.63 6.72%  THETA: $1.91 12.66%
THETA: $1.91 12.66%  MANTRA DAO: $3.65 0.01%
MANTRA DAO: $3.65 0.01%  Raydium: $6.12 1.26%
Raydium: $6.12 1.26%  Arweave: $22.32 26.33%
Arweave: $22.32 26.33%  Maker: $1653.82 0.91%
Maker: $1653.82 0.91%  Bitcoin SV: $70.39 3.93%
Bitcoin SV: $70.39 3.93%  KuCoin Token: $11.39 2.64%
KuCoin Token: $11.39 2.64%  Polygon: $0.56 20.61%
Polygon: $0.56 20.61%  Flow: $0.84 16.03%
Flow: $0.84 16.03%  Quant: $101.56 18.62%
Quant: $101.56 18.62%  Gala: $0.03 17.34%
Gala: $0.03 17.34%  Lido DAO: $1.35 9.64%
Lido DAO: $1.35 9.64%  EOS: $0.77 6.86%
EOS: $0.77 6.86%  Tezos: $1.14 3.31%
Tezos: $1.14 3.31%  Neo: $14.59 9.27%
Neo: $14.59 9.27%  Axie Infinity: $6.69 12.88%
Axie Infinity: $6.69 12.88%  Decentraland: $0.52 20.44%
Decentraland: $0.52 20.44%  The Sandbox: $0.42 16.24%
The Sandbox: $0.42 16.24%  Helium: $5.79 6.29%
Helium: $5.79 6.29%  Akash Network: $3.94 5.78%
Akash Network: $3.94 5.78%  GateToken: $11.00 8.3%
GateToken: $11.00 8.3%  AIOZ Network: $0.82 12.01%
AIOZ Network: $0.82 12.01%  eCash: $0.00 3.36%
eCash: $0.00 3.36%  Pendle: $5.34 6.37%
Pendle: $5.34 6.37%  MultiversX: $36.04 18.94%
MultiversX: $36.04 18.94%  Nexo: $1.35 3.06%
Nexo: $1.35 3.06%  Mina: $0.73 7.88%
Mina: $0.73 7.88%  FTX Token: $2.52 3.78%
FTX Token: $2.52 3.78%  Conflux: $0.17 12.07%
Conflux: $0.17 12.07%  Zcash: $48.21 5.63%
Zcash: $48.21 5.63%  Chiliz: $0.09 12.07%
Chiliz: $0.09 12.07%  IOTA: $0.22 17.38%
IOTA: $0.22 17.38%  Gnosis: $273.42 4.9%
Gnosis: $273.42 4.9%  Oasis: $0.10 15.49%
Oasis: $0.10 15.49%  Kusama: $43.35 98.88%
Kusama: $43.35 98.88%  XinFin Network: $0.05 15.36%
XinFin Network: $0.05 15.36%  SuperVerse: $1.33 8.76%
SuperVerse: $1.33 8.76%  PancakeSwap: $2.19 12.25%
PancakeSwap: $2.19 12.25%  Nervos Network: $0.01 8.25%
Nervos Network: $0.01 8.25%  Curve DAO Token: $0.50 11.2%
Curve DAO Token: $0.50 11.2%  Compound: $64.17 19.04%
Compound: $64.17 19.04%  Kava: $0.49 7.54%
Kava: $0.49 7.54%  TrueUSD: $1.00 0.12%
TrueUSD: $1.00 0.12%  NXM: $73.39 5.2%
NXM: $73.39 5.2%  Theta Fuel: $0.07 5.7%
Theta Fuel: $0.07 5.7%  DeXe: $8.32 0.22%
DeXe: $8.32 0.22%  1inch Network: $0.37 7.1%
1inch Network: $0.37 7.1%  Synthetix: $2.00 10.7%
Synthetix: $2.00 10.7%  Zilliqa: $0.02 15.53%
Zilliqa: $0.02 15.53%  WOO: $0.24 10.27%
WOO: $0.24 10.27%  Reserve Rights: $0.01 10.43%
Reserve Rights: $0.01 10.43%  Celo: $0.80 11.23%
Celo: $0.80 11.23%  Livepeer: $11.81 12.39%
Livepeer: $11.81 12.39%  Trust Wallet Token: $1.02 5.92%
Trust Wallet Token: $1.02 5.92%  IoTeX: $0.04 5.66%
IoTeX: $0.04 5.66%  Holo: $0.00 12.49%
Holo: $0.00 12.49%  Enjin Coin: $0.23 15.6%
Enjin Coin: $0.23 15.6%  Amp: $0.01 7.03%
Amp: $0.01 7.03%  Dash: $33.16 12.24%
Dash: $33.16 12.24% 








