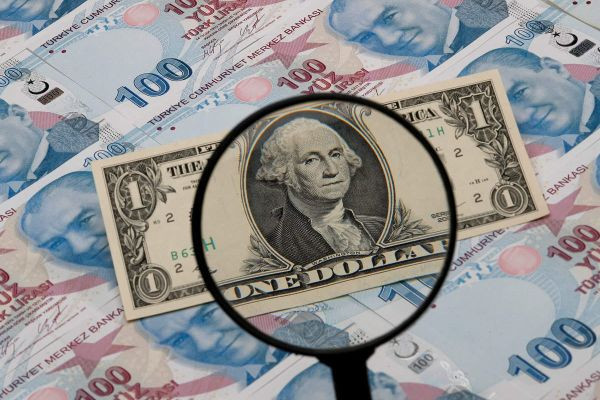
Introduction:
The United States dollar (USD) has long held its position as the world's most powerful currency, dominating global financial transactions and serving as the primary reserve currency for many nations. This article delves into the factors that contribute to the USD's status as the most influential currency in the world.
Historical Context:
The journey of the US dollar to its current position of dominance can be traced back to pivotal events in history. The Bretton Woods Conference of 1944 established the USD as the anchor currency for the international monetary system, setting the stage for its preeminence. The post-World War II era also witnessed the rise of the United States as a global economic powerhouse, further strengthening the dollar's position.
Challenges to USD Dominance:
Rise of Competing Currencies: The emergence of regional economic powers, such as China, has introduced viable alternatives to the USD. China's currency, the renminbi (RMB), is gaining acceptance in international trade and investment. As China's economic influence expands, the RMB has the potential to challenge the USD's dominance in global transactions.
Development of Regional Financial Systems: Countries are increasingly exploring regional financial systems that reduce reliance on the USD. Initiatives like the European Union's euro and Russia's efforts to establish an alternative payment system to bypass USD transactions indicate a shift towards diversifying currency usage.
Geopolitical Factors: Geopolitical tensions and conflicts can influence currency dynamics. Economic sanctions imposed by the United States have motivated some countries to seek alternatives to the USD to minimize exposure to potential disruptions in global financial systems.
Technology and Digital Currencies: The rapid advancement of financial technology has opened up new possibilities for digital currencies, including cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). These innovative forms of digital payment systems have the potential to disrupt traditional currency systems and redefine global financial transactions.
Economic Stability and Size of the US Economy:
One of the key reasons behind the USD's power is the stability of the US economy. Despite periodic fluctuations, the US economy has consistently demonstrated resilience, attracting investors and instilling confidence in the dollar. The sheer size of the US economy, characterized by its robust GDP and diverse sectors, further contributes to the currency's appeal.
Global Trade and Petrodollar System:
The US dollar's influence is bolstered by its pivotal role in global trade. Many commodities, including oil, are primarily traded in USD, creating a demand for the currency and reinforcing its global standing. The petrodollar system, established in the 1970s, solidified the dollar's position as the preferred currency for oil transactions, granting it a unique advantage over other currencies.
Financial Markets and Dollar-Based Instruments:
The depth and liquidity of US financial markets are unparalleled, offering a wide array of dollar-denominated instruments to investors worldwide. The US Treasury market, in particular, serves as a benchmark for global interest rates and a safe-haven investment destination during times of uncertainty. The widespread use of dollar-based financial products further solidifies the currency's dominance.
Geopolitical Influence and Soft Power:
The geopolitical influence of the United States plays a crucial role in maintaining the USD's status as the world's most powerful currency. The US government's stability, military strength, and diplomatic clout contribute to the overall perception of the dollar as a reliable and safe currency. Additionally, the global reach of American culture, media, and technology enhances the dollar's soft power and reinforces its global acceptance.
Challenges and Future Outlook:
While the USD's dominance remains undisputed, challenges exist that could potentially impact its status. Rising economic powers like China and the European Union seek to challenge the dollar's hegemony by promoting their own currencies. Additionally, the emergence of cryptocurrencies poses new questions regarding the future of traditional fiat currencies.
Implications of USD's Potential Decline
A decline in the USD's dominance could have far-reaching consequences. The value of the USD could be affected, impacting exchange rates, trade balances, and global investment flows. Central banks and financial institutions may need to adjust their reserve holdings, potentially diversifying away from the USD. Additionally, the United States could experience challenges in financing its deficits, as demand for its currency decreases.
However, a transition away from the USD would not be without challenges. The USD's infrastructure, liquidity, and stability have been built over decades, providing a strong foundation for global financial transactions. The network effects and trust associated with the USD may be difficult to replicate for any emerging alternative.
Conclusion:
The US dollar's position as the world's most powerful currency is a culmination of historical, economic, geopolitical, and financial factors. Its stability, size of the US economy, central role in global trade, financial market depth, and geopolitical influence have solidified its dominance. However, the evolving global landscape suggests that the future of the USD's supremacy may face new tests and transformations, warranting ongoing observation and analysis.
 Bitcoin: $98517.04 0.2%
Bitcoin: $98517.04 0.2%  Ethereum: $3463.86 4.48%
Ethereum: $3463.86 4.48%  Tether: $1.00 0.02%
Tether: $1.00 0.02%  Solana: $259.90 1.69%
Solana: $259.90 1.69%  BNB: $668.41 7.32%
BNB: $668.41 7.32%  XRP: $1.56 7.95%
XRP: $1.56 7.95%  Dogecoin: $0.46 13.11%
Dogecoin: $0.46 13.11%  Cardano: $1.11 19.5%
Cardano: $1.11 19.5%  USDC: $1.00 0.11%
USDC: $1.00 0.11%  Lido Staked ETH: $3447.24 3.97%
Lido Staked ETH: $3447.24 3.97%  TRON: $0.22 9.48%
TRON: $0.22 9.48%  Avalanche: $43.21 9.63%
Avalanche: $43.21 9.63%  Shiba Inu: $0.00 8.36%
Shiba Inu: $0.00 8.36%  Stellar: $0.52 74.56%
Stellar: $0.52 74.56%  Wrapped Bitcoin: $98218.48 0.26%
Wrapped Bitcoin: $98218.48 0.26%  Polkadot: $8.86 39.33%
Polkadot: $8.86 39.33%  Chainlink: $17.89 16.2%
Chainlink: $17.89 16.2%  Bitcoin Cash: $521.89 7.43%
Bitcoin Cash: $521.89 7.43%  UNUS SED LEO: $8.61 2.41%
UNUS SED LEO: $8.61 2.41%  NEAR Protocol: $6.45 13.82%
NEAR Protocol: $6.45 13.82%  Litecoin: $102.93 14.44%
Litecoin: $102.93 14.44%  Uniswap: $11.23 18.4%
Uniswap: $11.23 18.4%  Internet Computer: $11.80 15.8%
Internet Computer: $11.80 15.8%  Multi Collateral DAI: $1.00 0.13%
Multi Collateral DAI: $1.00 0.13%  Crypto.com Coin: $0.20 4.47%
Crypto.com Coin: $0.20 4.47%  Sp8de: $0.59 12.87%
Sp8de: $0.59 12.87%  Ethereum Classic: $30.55 9.31%
Ethereum Classic: $30.55 9.31%  VeChain: $0.05 37.31%
VeChain: $0.05 37.31%  Artificial Superintelligence Alliance: $1.43 15.64%
Artificial Superintelligence Alliance: $1.43 15.64%  Filecoin: $5.40 14.59%
Filecoin: $5.40 14.59%  Stacks: $2.12 9.84%
Stacks: $2.12 9.84%  OKB: $51.82 14.57%
OKB: $51.82 14.57%  Monero: $162.97 2.4%
Monero: $162.97 2.4%  Aave: $181.53 9.45%
Aave: $181.53 9.45%  Fantom: $0.93 30.19%
Fantom: $0.93 30.19%  Algorand: $0.31 27.22%
Algorand: $0.31 27.22%  The Graph: $0.25 16.58%
The Graph: $0.25 16.58%  Hedera Hashgraph: $0.16 22.5%
Hedera Hashgraph: $0.16 22.5%  Cosmos: $8.53 15.16%
Cosmos: $8.53 15.16%  Injective: $28.89 17.29%
Injective: $28.89 17.29%  THORChain: $5.88 11.58%
THORChain: $5.88 11.58%  THETA: $1.95 14.49%
THETA: $1.95 14.49%  MANTRA DAO: $3.73 2.86%
MANTRA DAO: $3.73 2.86%  Raydium: $6.06 0.59%
Raydium: $6.06 0.59%  Arweave: $23.38 32.18%
Arweave: $23.38 32.18%  Maker: $1682.70 1.93%
Maker: $1682.70 1.93%  Bitcoin SV: $72.31 7.43%
Bitcoin SV: $72.31 7.43%  Polygon: $0.60 29.52%
Polygon: $0.60 29.52%  KuCoin Token: $11.50 4.05%
KuCoin Token: $11.50 4.05%  Flow: $0.86 20.22%
Flow: $0.86 20.22%  Quant: $107.54 24.81%
Quant: $107.54 24.81%  Gala: $0.03 22%
Gala: $0.03 22%  Lido DAO: $1.37 11.76%
Lido DAO: $1.37 11.76%  EOS: $0.79 13.54%
EOS: $0.79 13.54%  Tezos: $1.18 9.07%
Tezos: $1.18 9.07%  Neo: $15.05 14.34%
Neo: $15.05 14.34%  Axie Infinity: $6.89 17.24%
Axie Infinity: $6.89 17.24%  Helium: $6.01 9.52%
Helium: $6.01 9.52%  Decentraland: $0.52 22.69%
Decentraland: $0.52 22.69%  The Sandbox: $0.42 18.88%
The Sandbox: $0.42 18.88%  GateToken: $11.34 11.36%
GateToken: $11.34 11.36%  Akash Network: $4.05 8.69%
Akash Network: $4.05 8.69%  AIOZ Network: $0.86 18.31%
AIOZ Network: $0.86 18.31%  eCash: $0.00 6.22%
eCash: $0.00 6.22%  Pendle: $5.48 9.54%
Pendle: $5.48 9.54%  MultiversX: $36.94 21.65%
MultiversX: $36.94 21.65%  Mina: $0.75 11.78%
Mina: $0.75 11.78%  Nexo: $1.36 3.78%
Nexo: $1.36 3.78%  FTX Token: $2.58 0.2%
FTX Token: $2.58 0.2%  Conflux: $0.18 14.69%
Conflux: $0.18 14.69%  Zcash: $49.59 9.84%
Zcash: $49.59 9.84%  Chiliz: $0.09 15.1%
Chiliz: $0.09 15.1%  IOTA: $0.22 23.7%
IOTA: $0.22 23.7%  Gnosis: $279.27 7.07%
Gnosis: $279.27 7.07%  Oasis: $0.10 20.16%
Oasis: $0.10 20.16%  SuperVerse: $1.37 12%
SuperVerse: $1.37 12%  XinFin Network: $0.05 16.56%
XinFin Network: $0.05 16.56%  PancakeSwap: $2.26 15.58%
PancakeSwap: $2.26 15.58%  Curve DAO Token: $0.52 15.71%
Curve DAO Token: $0.52 15.71%  Nervos Network: $0.01 10.11%
Nervos Network: $0.01 10.11%  Compound: $66.83 22.97%
Compound: $66.83 22.97%  Kava: $0.50 10.26%
Kava: $0.50 10.26%  Kusama: $33.40 53.78%
Kusama: $33.40 53.78%  DeXe: $8.75 4.4%
DeXe: $8.75 4.4%  TrueUSD: $1.00 0.04%
TrueUSD: $1.00 0.04%  Theta Fuel: $0.07 9.07%
Theta Fuel: $0.07 9.07%  NXM: $73.43 5.3%
NXM: $73.43 5.3%  1inch Network: $0.38 10.26%
1inch Network: $0.38 10.26%  Zilliqa: $0.02 18.56%
Zilliqa: $0.02 18.56%  Synthetix: $2.04 13.01%
Synthetix: $2.04 13.01%  WOO: $0.25 14.33%
WOO: $0.25 14.33%  Reserve Rights: $0.01 13.85%
Reserve Rights: $0.01 13.85%  Celo: $0.82 14.05%
Celo: $0.82 14.05%  Livepeer: $11.98 14.01%
Livepeer: $11.98 14.01%  Trust Wallet Token: $1.03 6.77%
Trust Wallet Token: $1.03 6.77%  IoTeX: $0.05 8.91%
IoTeX: $0.05 8.91%  Enjin Coin: $0.24 18.7%
Enjin Coin: $0.24 18.7%  Holo: $0.00 14.29%
Holo: $0.00 14.29%  Amp: $0.01 10.91%
Amp: $0.01 10.91%  Dash: $34.37 17.66%
Dash: $34.37 17.66% 








